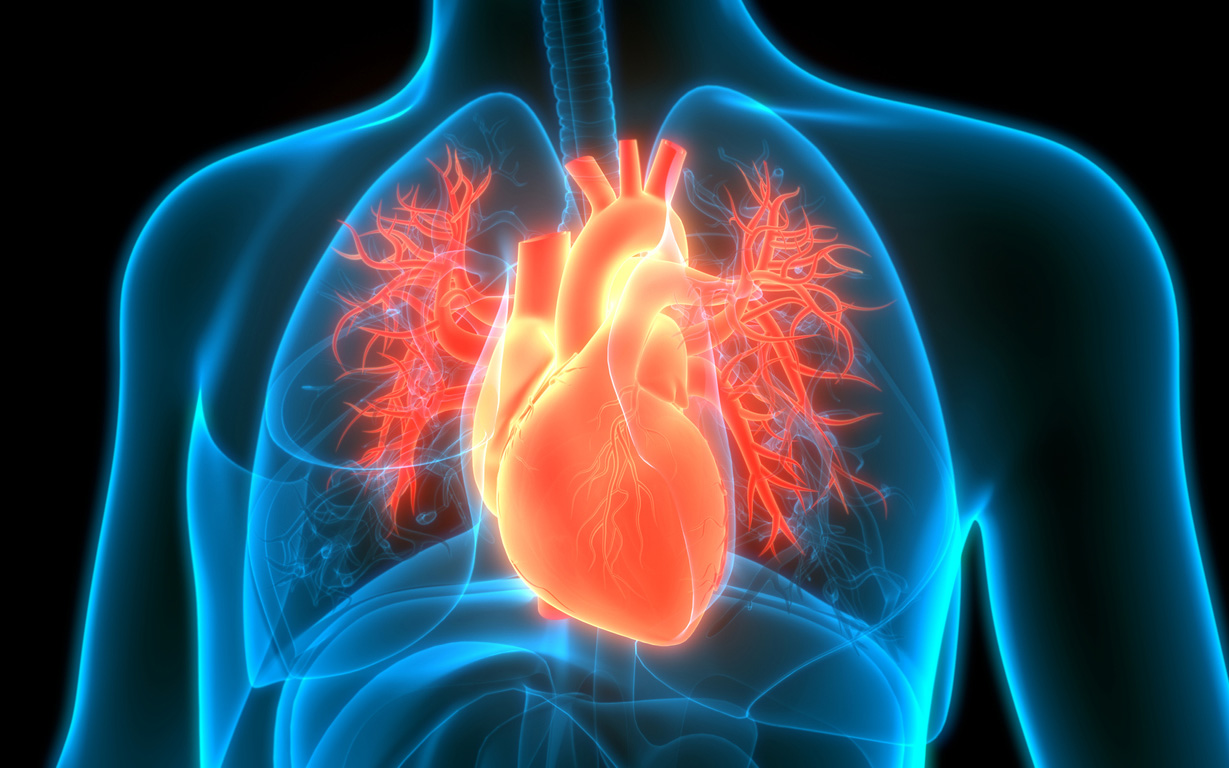
Heart
- Reporter 21
- 06 Nov, 2021
The heart is a vital organ in the human body, responsible for pumping blood throughout the circulatory system, supplying oxygen and nutrients to tissues and organs, and removing waste products. It plays a central role in maintaining life and is often referred to as the "engine" of the circulatory system.
Key aspects and functions of the human heart include:
Anatomy: The human heart is a muscular organ located in the chest, slightly to the left of the midline. It is roughly the size of a closed fist and is enclosed within a protective sac called the pericardium.
Chambers: The heart is divided into four chambers: two atria (right atrium and left atrium) and two ventricles (right ventricle and left ventricle). Atria receive blood returning to the heart, while ventricles pump blood out to the body and lungs.
Valves: The heart contains four valves that regulate blood flow. The atrioventricular valves (the tricuspid valve on the right side and the bicuspid or mitral valve on the left side) separate the atria from the ventricles. The semilunar valves (the pulmonary valve and aortic valve) control the flow of blood out of the ventricles into the pulmonary artery and aorta, respectively.
Blood Flow: Deoxygenated blood returns from the body and enters the right atrium, then flows into the right ventricle and is pumped to the lungs for oxygenation. Oxygenated blood returns from the lungs to the left atrium, flows into the left ventricle, and is then pumped out to the rest of the body through the aorta.
Cardiac Cycle: The cardiac cycle is the sequence of events that occurs with each heartbeat. It involves the contraction (systole) and relaxation (diastole) of the atria and ventricles, allowing blood to flow efficiently through the heart and circulatory system.
Electrical System: The heart has its electrical conduction system that regulates its rhythm. The sinoatrial (SA) node, located in the right atrium, acts as the natural pacemaker, initiating electrical impulses that coordinate heart contractions.
Circulatory System: The heart is the central pump of the circulatory system, which includes blood vessels (arteries, veins, and capillaries) that carry blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to cells and removing waste products.
Heart Rate and Blood Pressure: Heart rate (the number of heartbeats per minute) and blood pressure (the force of blood against the walls of arteries) are vital signs that reflect the heart's functioning and overall health.
Cardiovascular Diseases: Heart diseases, such as coronary artery disease, heart failure, and arrhythmias, can impair the heart's ability to function properly and can have serious health consequences.
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR): CPR is an emergency procedure used to manually pump the heart and provide oxygen to the brain and other vital organs in cases of cardiac arrest.
The heart's role in pumping oxygen-rich blood to the body's organs and tissues is essential for maintaining life and overall health. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, is important for promoting heart health and reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Prince Mahmud
great post
Prince Mahmud
Awesomr
Prince Mahmud
Great